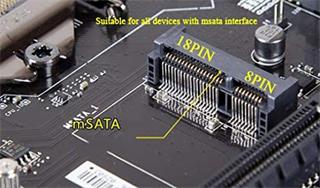
An mSATA SSD is a solid-state drive (SSD) that conforms to the mSATA interface specification developed by the Serial ATA (SATA) International Organization.
An mSATA SSD has a smaller form factor than a standard SSD and is designed for use with portable, power-constrained devices such as laptops, tablets and netbooks. The mSATA SSD has also seen use in commercial products such as digital signs, point-of-sale devices, retail kiosks and multifunctional printers.
An mSATA SSD is roughly the size of a business card. Advantages of mSATA SSDs include the small form factor, low power consumption, shock/vibration resistance and fast boot/shutdown capabilities. The maximum bandwidth of an mSATA SSD is 6 gigabits per second (Gbps).
Specification for mSATA
The mSATA specification describes how to map SATA signals onto a Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) mini-card connector to enable use with a wide range of applications.
Like SATA, mSATA uses the Advanced Technology Attachment (ATA) command set to transfer data between a host computer and target storage device. The main differences between an mSATA SSD and a SATA SSD are physical size and the connector.
The SATA International Organization (SATA-IO) started development of the mini interface connector in 2009. The mSATA specification emerged in 2011 as part of SATA revision 3.1. Vendors who contributed to the mSATA specification included Dell, Hewlett-Packard (now known as Hewlett Packard Enterprise), Lenovo, Samsung, SanDisk, sTec (which was acquired by HGST, a Western Digital company, in 2013) and Toshiba.
SATA-IO initially referred to the specification as mini-SATA, but the organization later simply called it mSATA.